Understanding the 2024 Evolution of Consumer Behavior in Middle East E-commerce
Table of Contents
With the rapid growth of e-commerce in the Middle East, understanding consumer behavior has never been more crucial. As businesses strive to stay ahead, they must recognize and adapt to the evolving preferences of their audience. This evolution is not just a trend but a reflection of the socio-economic changes, technological advancements, and cultural shifts in the region.
Today, the Middle Eastern consumer is more informed, discerning, and empowered than ever before. With a plethora of choices at their fingertips, businesses must go beyond traditional selling tactics to truly resonate with their audience. Let’s delve deeper into the psyche of the modern Middle Eastern shopper.
Resonating with the Modern Middle Eastern Shopper
Every e-commerce business owner knows the challenge: you’ve set up a sleek online store, stocked it with top-notch products, but the expected flood of customers is more of a trickle. Why? Because understanding the consumer is the key. The Middle Eastern market, with its unique blend of tradition and modernity, demands a nuanced approach.
It’s not just about selling a product; it’s about telling a story, building trust, and offering value. The modern Middle Eastern consumer seeks authenticity, relevance, and convenience. They are not just buying a product; they are buying an experience, a lifestyle. And this is where understanding their behavior becomes paramount.
A Tale of Two Shoppers
Imagine Sarah, a young professional from Dubai. She’s tech-savvy, values sustainability, and is always on the lookout for the latest fashion trends. She represents the new age Middle Eastern consumer who is globally aware yet locally rooted. On the other hand, there’s Ahmed from Riyadh, who prioritizes value for money and relies heavily on user reviews before making a purchase. He embodies the traditional shopper, cautious and value-driven.
Both Sarah and Ahmed are regular online shoppers, but their buying behaviors are distinct. Recognizing these nuances is the first step to crafting a successful e-commerce strategy. Catering to their individual needs, preferences, and pain points can make all the difference in converting a casual browser into a loyal customer.
Life Beyond Traditional Shopping
Imagine a world where every online shopping experience is tailored to individual preferences. Where businesses anticipate needs, offering products and services that resonate deeply with their audience. This is the potential of truly understanding consumer behavior in Middle East e-commerce.
But achieving this vision requires a shift in perspective. It’s not just about selling products; it’s about building relationships. It’s about understanding the cultural, social, and economic factors that influence buying decisions and crafting strategies that align with these insights.
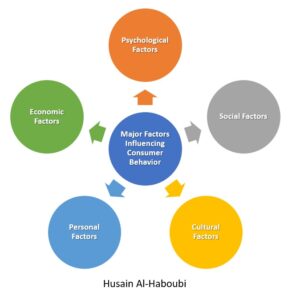
Major Factors Influencing Consumer Behavior
Consumer behavior is a multifaceted phenomenon influenced by a myriad of factors. These factors play a pivotal role in shaping the purchasing decisions of consumers. Understanding these determinants is crucial for businesses aiming to resonate with their target audience and tailor their offerings effectively. Here are the major factors that influence consumer behavior:
- Psychological Factors: Human psychology plays a significant role in determining consumer behavior. Factors such as motivation, perception, learning, and attitudes and beliefs can greatly influence a consumer’s buying decision. For instance, a consumer’s motivation can be driven by various needs, from basic necessities to self-actualization. Perception, on the other hand, is shaped by the impressions consumers form about a product based on advertisements, reviews, and other sources of information. Learning, which comes from experience, and attitudes and beliefs, which are deeply ingrained, further shape the consumer’s approach to products and services.
- Social Factors: Social interactions and the environment in which a consumer is raised play a crucial role in shaping their buying behavior. Factors such as family influence, reference groups, and roles and status in society can determine the products a consumer gravitates towards. For example, a person’s buying behavior can be influenced by their family’s preferences or the opinions of their peer group.
- Cultural Factors: Cultural norms and values significantly influence consumer behavior. This includes broader cultural influences, subcultures (like religion, nationality, or region), and social classes. Each of these can have distinct preferences, beliefs, and buying behaviors. For instance, a consumer from a particular cultural background might prioritize certain product attributes over others due to cultural significance.
- Personal Factors: Individual characteristics such as age, income, occupation, and lifestyle also play a role in shaping consumer behavior. For example, a teenager might prioritize trendy fashion items, while a middle-aged individual might focus on buying property or vehicles for the family.
- Economic Factors: The economic environment, both on a macro and micro level, can influence consumer buying habits. Factors such as personal income, family income, consumer credit, liquid assets, and savings determine the purchasing power of a consumer. For instance, in a prosperous economic environment, consumers are more likely to make luxury purchases, while in a downturn, they might prioritize essential goods.
Steps to Align with Evolving Consumer Behavior
- Embrace Digital Transformation: The digital revolution has transformed the way consumers shop. With the rise of digital-first consumers, businesses must enhance their online presence, offer seamless shopping experiences, and leverage data analytics to gain insights into consumer preferences.
- Personalized Marketing: In an age of information overload, personalization stands out. Use consumer data to craft personalized marketing campaigns, ensuring relevance and increasing engagement. It’s about delivering the right message to the right person at the right time.
- Focus on Value: Economic uncertainties, coupled with a discerning consumer base, have made value paramount. Offering value-driven solutions, both in terms of quality and price, can be a game-changer in the competitive e-commerce landscape.
- Sustainability Matters: The modern consumer is socially conscious. Emphasizing sustainability, ethical practices, and corporate responsibility can set your business apart. It’s not just about being eco-friendly; it’s about being socially responsible and showcasing that commitment.
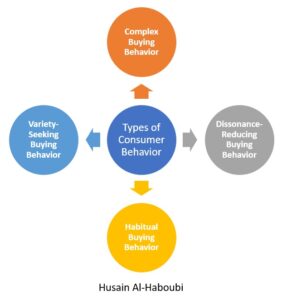
What are the 4 types of consumer behavior?
Consumer behavior can be categorized into four types. Here are the types of consumer behavior:
- Complex Buying Behavior: This occurs when consumers are highly involved in a purchase and perceive significant differences among brands. For example, buying a car requires extensive research and comparison.
- Dissonance-Reducing Buying Behavior: Here, consumers are highly involved but see little difference among brands. For instance, choosing between two similar washing machines can lead to post-purchase anxiety.
- Habitual Buying Behavior: Low consumer involvement and little perceived brand difference. For example, buying the same brand of bread every week without much thought.
- Variety-Seeking Buying Behavior: Low consumer involvement but significant perceived brand differences. For instance, trying a new flavor of chips just for the sake of variety.
What are the 5 characteristics of consumer behavior?
The five key characteristics of consumer behavior include:
- Problem Recognition: The initial step where a consumer identifies a need. For example, realizing one’s smartphone is outdated when a new model is launched.
- Information Search: Once a problem is recognized, consumers seek information. This could involve online research, reading reviews, or asking friends about their experiences.
- Evaluation of Alternatives: Consumers compare different products or brands to determine the best fit for their needs. For instance, comparing features of two smartphones before making a purchase.
- Purchase Decision: After evaluating alternatives, the consumer makes the buying decision. However, external factors like a sales promotion can influence this decision.
- Post-Purchase Behavior: After purchasing, the consumer will experience satisfaction or dissatisfaction. A positive experience can lead to brand loyalty, while a negative one can result in returns or negative reviews.
Engaging with the Future of E-commerce
As the e-commerce landscape in the Middle East continues to evolve, businesses must stay agile, continuously adapting to the changing needs and preferences of their consumers. By deeply understanding and resonating with these shifts, businesses can not only survive but thrive in this dynamic market.
For those looking to delve deeper into the world of e-commerce in the region, consider reading A Beginner’s Guide to Opening an E-commerce Website in Saudi Arabia.
Further Reading
For a comprehensive understanding of the e-commerce landscape in the Middle East, consider exploring reports from authoritative sources such as McKinsey and Deloitte. These institutions offer in-depth insights, trends, and forecasts that can guide businesses in crafting effective strategies for the future.